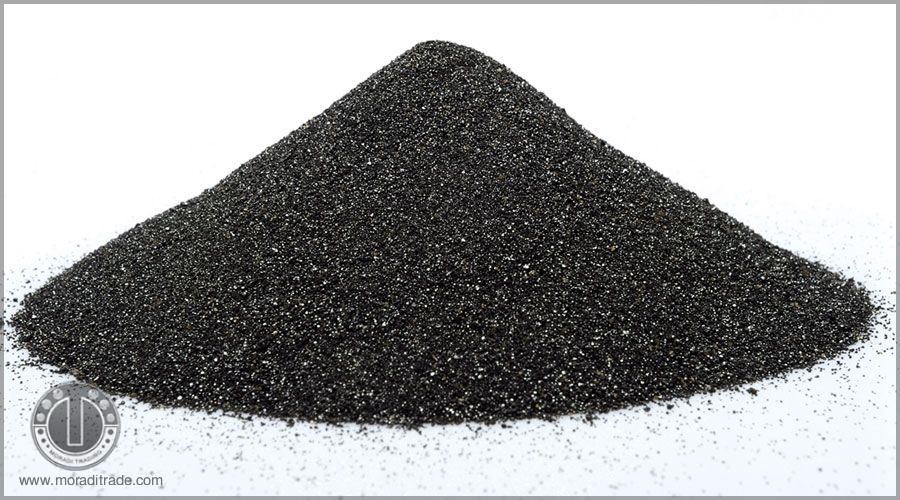
Chromite Sand
Chromite Sand is a naturally occuring spinel consisting primarily of the oxides of chrome and iron.
Mineral services of Behravan Sanat Kharazm:
Owning several mines in Khorasan Razavi and South Khorasan provinces, we are active in the following fields:
- Processing of minerals such as concentrate and chromite sand
- Owning copper, gold, and chromite mines, and attracting investors for the mines
Specialized mining services:
Chromite Sand production with different chromium grades and custom-made minerals with variouse grain sizes.
Chromium
Chromium is a hard, brittel, silver-colored metals discovered in 1798 by V.L.Vauquelin. This element, along with molybdenum and tungsten, is in the sixth group of the periodic table of elements. The chromium element is not found free in nature. The most important mineral containing chromium in the nature is chromite (FeO.Cr2O3).
Chromite uses:
Chromite ore is the only supplier of chromium, which is highly valued for the production of alloys and the preparation of special steels. Chromium and chromite have different direct and indirect uses and are used extensively in a wide range of modern industrial systems.
Chromite Sand product uses
Its properties enable the material to be used in high duty grey iron and steel foundries as core and mould making sand. Its high thermal conductivity gives it good chilling properties, low thermal expansion gives rise to good dimensional stability. Its basicity being close to neutral allows the use of a wide range of resin bonding systems and inorganic binders, it has a high refractoriness and a broad sieve distribution.
In steel production, Chromite Sand is used as well filler for protection of the sliding gate in large steel holding ladles.
When ground to a fine flour, Chromite Sand is used for the production of green glass beverage containers.
Grade types of chromites sand:
Grade A: Includes chrome shifter and over 64% of chromites with high Chrome (ratio Cr/Fe < 5/2)
Grade B: Includes 56-64% chromium and grade chromites ratio of 5/2 iron (Cr/Fe = 8/1-5/2 )
Grade C: Includes 50-55% chromium and grade chromites with high ratio of iron (Cr/Fe > 8/1)
Types of chromite sand grain:
- Coarse-grained (grain size greater than 3 mm)
- Medium grained (grain size between 3 to 0.7 mm)
- Granule-grained (grain size smaller than 0.7 mm)
Main Chromite uses:
- Metallurgy 2. Chemical industry 3. Refractories
Metallurgy
The most important use of chromium is in the metallurgy and electroplating industry. Chromium is an element that is resistant to heat, scratches, corrosion and oxidation, and stainless steels and alloys made of chromium have a high hardness, compressive and bending strength.
chemical industry
The most important chemical derivatives of chromium are sodium bicromate, sodium chromate, sodium bicromate, potassium chromate, potassium bichromate, chromium acid, Chrome alkaline sulfate and chromosal. Commonly used in the chemical industry are chromites that have a Cr / Fe ratio of more than 2/2 in their composition with less than 8% silica. About 15% of the world's chromites are consumed in the chemical industry.
Refractories:
30 to 35 percent of the extracted chromite in the world is used in the refractory industry, which is generally used for the production of refractory bricks and refractory materials, as well as the production of casting sands. Chromite refractories’ typical chemical include 31 to 45 percent of chromium oxide, 24 to 35 percent alumina, 14 to 20 percent magnesium oxide, 12 to 20 percent bicarbonate oxide, 3 to 6 percent silica, and less than 1 percent calcium oxide. Some Magnesium oxide is also added to their raw material.
The main uses of chromite in the casting industry are:
- In the manufacturing of furnace wall cubicles and auxiliary melting furnaces and use as a refractory material.
- As a sand suitable for casting for the production of: a) casting steels, especially manganese steel; b) large cast iron parts; c) sand blasting in the production of cast iron parts;
- use of chromite powder for the preparation of some initial refractory slurries for precision casting and chromite sand as refractory.
- Important uses of chromite are in metallurgy, refractory and chemical industries. The grade needed for uses in metallurgy and chemical industries is high, but it can be low in refractories.
- Chromite has good properties for casting. These features and advantages include:
- a) good thermal stability (high melting point); b) high thermal conductivity in comparison with silica sand; low and uniform thermal expansion; longer life and chemical neutrality; c) After casting and cooling, chromite sand is easily removed from the surface of the unit (not absorbed by the melt) -; Frequent use of chromite grains in the casting
Chromite selection as casting sand depends on several parameters, including:
- Its availability
- Price
- Types of casting as well as the type of mineral to be moldeds
- Casting techniques
Chromite Sand properties
- Melting point of 2150°C
- Good thermal conductivity
- Good resistance to thermal shock
- Excellent resistance to metal penetration or burn-on
- Resists slag attack
- High dimensional stability
1-Geology & Exploration: Remote Sensing:
- Geophysics
- Geochemistry
- Geology
2-Mine planning & Design:
- Mineral mass produced three-dimensional model
- Optimum pit design based on technical and economic studies
- Provide long-term plans and short-term extraction
- Network design, drilling and blasting
- Mapping projects
- Preparation of production reports
- Sustainability studies of the walls of mines
- The grade distribution model and calculation of statistical factors
- Statistical tests and calculations of CI and low-scale data
- Reserve estimates undertaken in different ways for low grade and high grade areas and grade error variance estimation
3-Mineral Processing:
- Iron
- Copper
- Chromite